In the recent past, cyber-attacks have increased tremendously with flaws in software and hardware making it easy for cybercriminals. It is common to read reports of massive data breaches, Ransomware, and IoT attacks. Cyber-attacks have gone a notch higher and it is common to find highly funded cyber warriors who are paid to compromise critical infrastructures, gather intelligence, steal intellectual property and technology used in defense to mention a few. Organized cyber criminals have caused havoc all over the world and one of the latest victims is an American IT company called SolarWinds.
The recent massive cyber breach left many systems running SolarWinds Orion software exposed and others compromised. The Cyber Unified Coordination Group (UCG), a joint security investigating team from all security departments, was formed to investigate one of the largest cybersecurity attacks on critical federal government arms and other private networks. Approximately 18,000 SolarWinds Orion customers were affected directly according to the preliminary investigation by UCG. APT29, a Russian hacker group, was suspected to be behind these attacks after much investigation.
How it happened
This was a typical example of what is called a supply chain attack where a third-party service provider is targeted by hackers to launch an attack in organizations that have procured their service. Due to high-security measures that have been put in place by government agencies and private entities in defending data and networks, cybercriminals are now using vendors to launch attacks on these entities as opposed to attacking them directly. With sophisticated tools, they can easily exploit vulnerabilities in hardware or software supplied by third parties and gain access through them to penetrate the network and IT systems.
Take the example of SolarWinds, the attackers exploited a vulnerability in one of the Orion software update processes and installed a malware called SunBurst as part of the vendor package. It was installed in the victim’s systems and it waited for a few weeks before it could become active. This malware was designed to remain for a long time in the system without being detected through hiding as a legitimate Orion Service. It would in the meantime collect commands that are used in these systems and communicate over HTTP to predetermined Urls where attackers could gather more information on their targets.
The attackers would then use stolen credentials to log into the systems remotely and deploy customized backdoor tools (unauthorized access into the system). They would then sit in the system patiently while studying the environment waiting for the right moment to strike. The UCG investigations concluded that the attack could have been ongoing for several months before it was finally detected. Cybercriminals who are well funded can stay under the radar collecting and gathering information before they can finally attack and if they don’t get caught organizations will not notice they are being attacked.
Below is a diagram showing how SolarWinds Sunburst attack was perpetrated
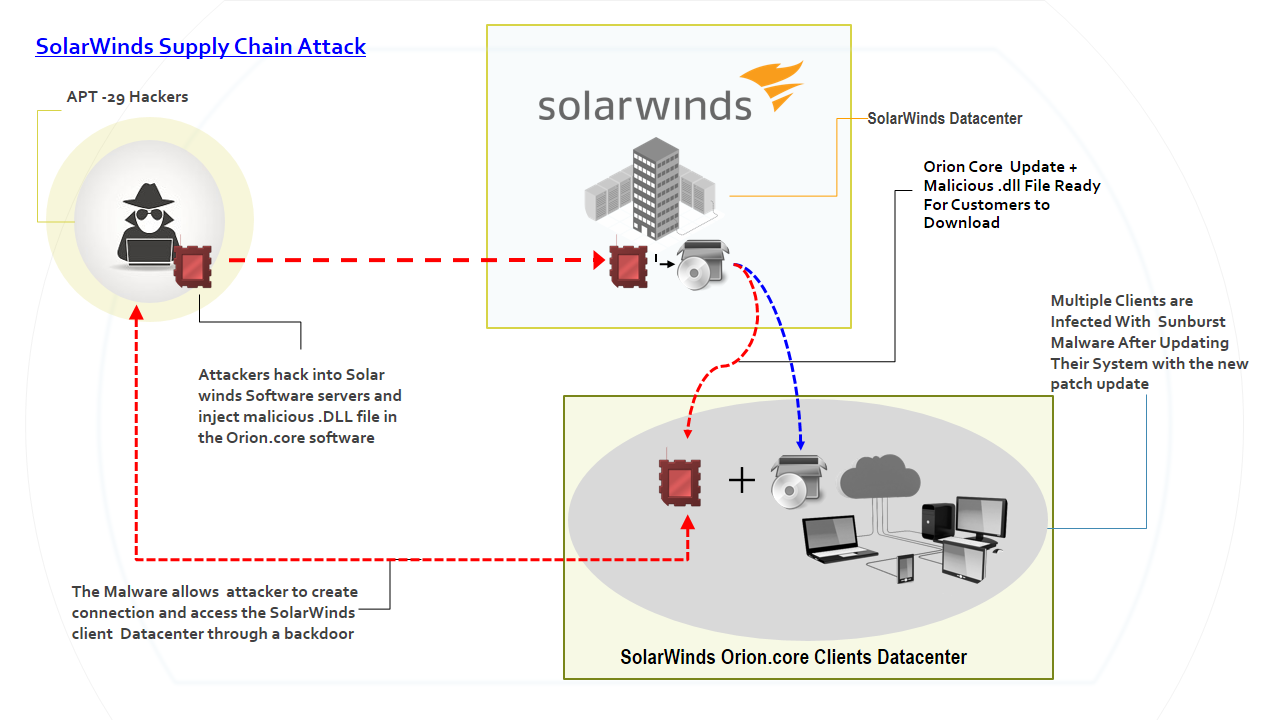
Figure 1 SolarWinds Sunburst attack
SolarWinds Response to Sunburst attack
All companies that develop software or manufacture hardware are prone to supply chain attacks. SolarWinds being one of the biggest tech company’s producing monitoring software for large corporate and government entities, they became a prime target for these attackers. After this attack, the company started its own internal investigation and came up with the following measures to stop further attacks on its software. These measures which were disclosed by SolarWinds CEO Mr. Sudhakar Ramakrishna in the company blog;
- Revoking of code signing certificates that were used to sign the compromised software versions from March 8th
- Consolidation of both remote and cloud access to the SolarWinds network and enforcing multi-factor authentication.
- Use of other third-party security tools for analysis of the source code for their Orion platform software
- Hiring penetration testing services for the company to easily identify any security issue arising across its portfolio.
- Deployment of additional threat detection, protection on the entire network which also includes its production environment.
- Setting up a team of experts to help clients who might need to upgrade or apply updates hotfix on their Orion Platform product without incurring any charges.
How to prepare for similar cyber attacks
Cyberspace continues to grow and it’s therefore important for every organization to be well prepared in case of an attack like SolarWinds. Criminals are consistently acquiring a lot of skills and infrastructure and it is therefore impossible to block such attacks entirely. However, it is possible to detect the likelihood of an attack in the future by following these security best practices;
- Testing of Information Technology Systems that are used in corporations to assess whether they can be exploited or the measures which should be taken to minimize risk exposure.
- Develop patch management plans where patching is done in a test environment before it can fully be deployed on the system.
- Demanding security measures from third-party vendors to be put in place and before any vendor is brought on board due diligence should be conducted.
- Implementation of in-depth defense and zero-trust security models can help in easily detecting attacks in case one security measure fails to do the same.
- Implementation of multi-factor authentication means even though an attacker has stolen user credentials it will not be easy to access organization resources with other methods of verification used in MFA.
Summary
It is clear from the SolarWinds case study, any organization is prone to attacks at any moment and the damage can have far-reaching consequences. Solarwinds became one of many victims of cybercrime and surprisingly, many other companies could be in a similar position it’s just they are not aware of the attack launched against them. This security breach has exposed many companies and government agencies and damaged SolarWinds’ reputation. It’s therefore, necessary for organizations to learn their deficiencies early and establish actionable improvements which should be done regularly.
SolarWinds and other companies that were compromised by this attack have probably some of the best cyber defense teams. Unfortunately, the Sunburst malware was still able to find its way in many networks without being noticed until it was too late. This attack has exposed how susceptible organizations are to hacking and therefore the need to put critical controls in place. This must be supported by the highest level of management through a commitment to cybersecurity models that work.

